Table of Contents
Designers and engineers often need software to adapt, repair, and finalize 3D models for 3D printing. But before finalizing, they might need to repair STL files. Luckily, the era of manual mesh programming is long gone.
Today, various specialized tools are available with automatic and manual STL repair capabilities. For most models, automatic wizards will be sufficient to correct minor flaws like holes and loose shells. However, models with more deep flaws will need a stand-alone solution.
In this guide, we’ll go over the STL file repair process and show you how to use five of the best STL repair programs to fully fix models, so they’re ready for 3D printing.
How to Repair STL Files with Free STL Repair Tools
What is the Purpose of Repairing STL File
3D designers typically build models using complex surfacing techniques. As a result, curves and splines define “perfect” geometry mathematically. Surfaces are transformed into a mesh format for 3D printing, representing geometry as a network of connected triangular faces and vertices.
Mesh conversion is similar to breaking a perfectly smooth mirror, then gluing all the pieces back together to restore the mirror’s original appearance. If the 3D print is done correctly, it produces a manifold mesh that is flawless and identical to the original design. If it’s done incorrectly, the model will have numerous edges, holes, and floating pieces in addition to regions where multiple intersecting triangles should not be.
How to Repair STL Files with Free STL Repair Tools
How to Repair STL File
Here are the steps that make up a typical STL file repair workflow:
- Auto-repair. The STL repair software wizard will try to correct all significant errors, such as holes, separate shells, and intersections.
- Separating shells. A mesh is made up of groups of connected triangles. It may have several continuous surfaces that should ideally be joined together, and any outdated surfaces should be removed.
- Closing holes, bridging gaps. Some detailed STL repair programs support a variety of hole filling techniques, including planar, tangent, ruled, and freeform.
- Resolving overlaps and intersections. Usually, this necessitates completely recalculating the mesh.
- Eliminating triangles with sharp, narrow angles, double faces, and double vertices.
- Stitching remaining holes and exposed edges.
- Manual repair by removing and adding triangles.
- Remeshing to reduce triangle count.
- Exporting data in the selected mesh format.
We will use STL (StereoLiThography), the most widely used and storage-friendly format, in this article. We advise keeping the. STL files should be saved in binary format to further reduce file size. Other helpful formats with specialized features for storing material, color, rendering, 3D scanning, and 3D printing information include AMF, Collada, OBJ, and PLY, as described in our Meshmixer tutorial.
Meshmixer is the best STL repair tool, according to our research. It combines an intuitive user interface with all the tools required to fix intricate mesh errors. The fact that it offers more options and is free makes it the clear leader. In addition to editing STL files and reshaping entire sections, Meshmixer is a helpful tool for optimizing and finishing 3D models. Check out our Meshmixer tutorial for 15 expert hints on how to edit STL files for 3D printing.
Engineers are the target audience for Autodesk’s Netfabb, which stands out thanks to its sophisticated 3D printing setup capabilities.
Despite offering a vast range of STL file repair functions and being a professional STL editor solution, Magics frequently necessitate more manual STL repair work. Magics thus takes the third spot on the list.
Even though Blender is more suited to 3D modeling and has a complicated interface, it still provides the majority of the functionalities needed for effective STL repairs.
Finally, Meshlab is a must-have lightweight mesh viewer and editor that, thanks to its sophisticated remeshing scripts, makes up for what it lacks in file repair functionality and user friendliness.
How to Repair STL Files with Free STL Repair Tools
Tutorials for Advanced STL Repair Software
The five STL repair tools are tested in the next section using a challenging 3D coat hook model with numerous significant flaws, including holes, gaps, intersections, and floating triangles. A mounting cylinder and the hook must be combined to create a single watertight mesh.
Follow along as we go through the five best STL repair programs step by step.
How to Repair STL Files with Free STL Repair Tools
Meshmixer

An intuitive and flexible mesh editing program is Meshmixer. Not only can a triangle mesh be optimized, but it can also be stylized, add useful features, and have entire sections resculpted.
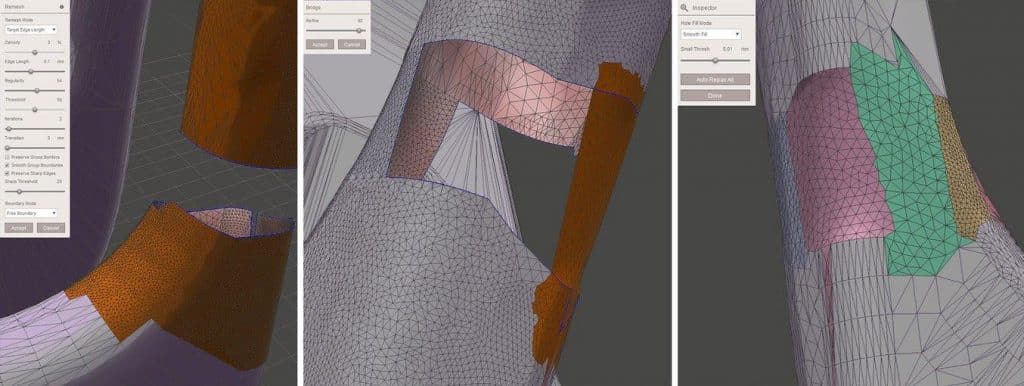
We discover that “Analysis > Inspector” does display all mesh errors after loading the coat hook into Meshmixer. Before correcting individual errors by clicking on the dot indicators or running “Auto Repair All“, which typically suffices, make sure to choose the appropriate “Hole Fill Mode“. For improved visibility, select the X-ray mode under “Shaders“.
Alternatively, you can use the “Edit > Erase and Fill (F)” operation from the popup menu to fix the hole by selecting the area around it. The “Type” parameter produces a good continuous fill when set to “Smooth MVC“. The options “Edit > Make Solid” and “Edit > Replace and Fill” also produce a closed mesh. The improved area will seamlessly merge into the model with one more pass of the “Robust Smooth” sculpting brush.
If the model consists of separate shells, select “Edit > Separate Shells” and then press “Ctrl + Shift + O” to launch the object browser. Select two shells one at a time moving forward, then click “Boolean Union” in the popup window. The intersection curve between the two objects will be maintained in the newly opened submenu’s “Precise” or “Max Quality” mode. While “Fast Approximate” is much quicker and typically sufficient.
Two red objects are produced if the Boolean operation fails. Then, to improve your chances of success, increase the “Search Depth” parameter and decrease the “Target Edge Scale“. Utilizing intersection curves increases quality as well. If all else fails, adjusting one of the shells in the “Edit > Transform” section by a few hundredths of a millimeter will solve the problem.
“Auto Repair All” will fix all boundary loops and eliminate floating sections. We want to manually join the space between two struts in this situation. Since this is a gap between circular loops, it is best patched up in sections and works best on straight sections. The “Bridge” tool can be used in this situation. Select “Edit > Select” and select the triangles you want to connect on either side. When the popup menu appears, select “Edit > Bridge (Ctrl + B)” and increase the “Refine” parameter to a level that will ensure a stable connection. For a few spots around the gap’s edge, issue the “Bridge” command again. Then, give the “Inspector” command to fill the remaining holes. Using “Edit > Remesh” before repairs increases and homogenizes. Triangulation in the affected area is a reasonable error prevention technique.
How to Repair STL Files with Free STL Repair Tools
Meshlab

Meshlab is a software package that offers numerous triangulation and cutting-edge repair algorithms. It focuses on mesh operations related to 3D scanning data. One helpful method to recalculate a mesh towards a target number of faces is “Filters > Remeshing, Simplification and Construction > Simplification (Quadratic Edge Collapse Decimation)“. “Filters > Cleaning and Repairing > Merge Close Vertices” is a different triangle reduction method. Flat surfaces will be best preserved if “Planar Simplification” is checked.
By selecting “Split in Connected Components” from the context menu, you can identify floating elements when you right-click the part in the project window. Then, using a “Union” operator with CSG Operation, separate shells can be deleted one at a time or recombined.
With Meshlab, simple mesh repairs are also possible. For instance, all intersecting triangles will be selected by the filtering option “Filter > Cleaning and Repair > Select Self Intersecting Faces > Apply“, which can then be eliminated by pressing “Delete. Filters > Cleaning and repairing > Remove Duplicated Faces and Remove Duplicated Vertex” actions are always beneficial. Filling in holes using “Filters > Remeshing, Simplification and Construction > Close Holes” is the next step. When a mesh is not watertight, the Compute Geometric Measures operation under “Filters > Quality Measure and Computations” will let you know. If not, use “Render > Show Non Manif Edges and Show Non Manif Vertices” to identify the affected regions.

Using the “Select Faces in a Rectangular Region” tool from the toolbar, groups of triangles can be removed to fill in gaps. To exclude backfaces from the selection, hold down the Alt key; to deselect, press Shift + Ctrl + D. Use the “Z-Painting” tool on the toolbar to select the red brush icon to pick out specific triangles. Triangles can be chosen using the left mouse button, then deleted using the right mouse button.
We turn to the surface generation technique under “Filters > Remeshing, Simplification and Construction > Surface Reconstruction: VCG” because Meshlab does not include triangle creation functions. “Filters > Remeshing, Simplification and Construction > Screened Poisson Surface Reconstruction” is typically preferred over this approach. A smooth manifold mesh will be produced with a low enough setting for “Voxel Side” and a high enough value for “Geodesic Weighting and Volume Laplacian Iterations.“
A different approach is to generate an “Alpha Complex” and then an “Alpha Shape,” which can occasionally work with the appropriate values. Under “Filters > Remeshing, Simplification and Construction > Uniform Mesh Resampling“, Meshlab provides a voxeliser for remesh operations that yields a manifold mesh and an offset helpful parameter for producing hollow parts.
Note: After each significant operation, save the meshes! Since there is no undo feature in Meshlab, you must import the original mesh again.
How to Repair STL Files with Free STL Repair Tools
Magics

A specialized tool called Materialise Magics for 3D printing allows for extensive manual control over meshes, including wall thickness analysis, hollowing, remeshing, smoothing, Boolean, and cutting operations, as well as fixing holes, imperfect edges, and the most challenging triangle errors.
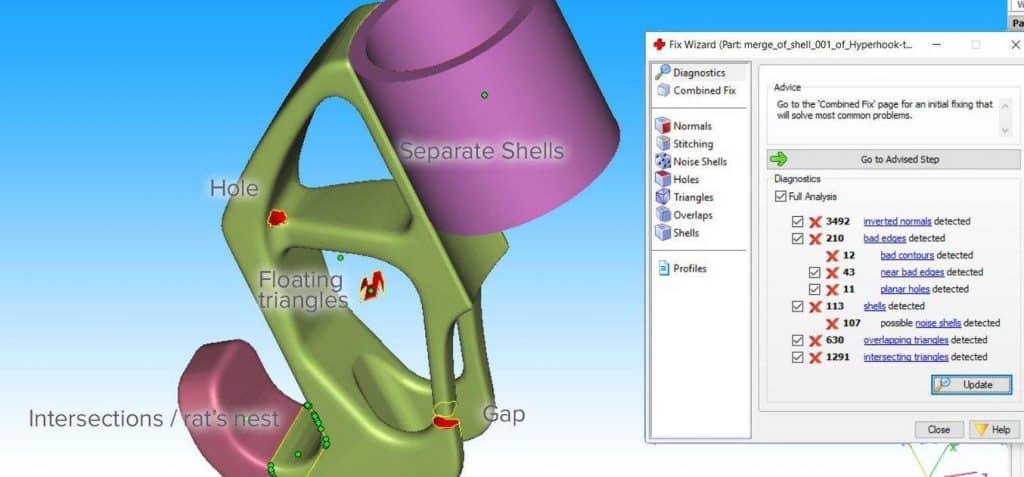
Errors are frequently fixed by using the “Fix Wizard” found under the red cross icon. A diagnostics table is opened when you click “Go to Advised Step” to check for various errors that must be fixed. Unchecking “Overlapping” triangles and “Intersecting triangles” for large meshes is advised in favor of correcting the most serious issues first. Most errors will be fixed if you choose Update, then click “Go to Advised Step” and “Automatic Fixing.”
Suppose the fix wizard is unable to fix imperfect edges and overlapping triangles. In that case, the “Stitch” function under “Stitching” in the “Fix Wizard” menu frequently proves helpful. Run the Fix Wizard once more or select Detect “Overlapping” from the Overlaps menu to find any remaining overlapping triangles. By clicking “Delete Marked” ,all overlaps are chosen and will be deleted. Similar operations can be carried out under “Triangles > Detect Intersecting” for intersecting triangles. The “Create” button enables manually filling in the remaining gaps if stitching the remaining gaps does not finish the repair. Additionally, manually marking mesh sections is possible using the “Marking” tab on the main menu.
Under “Noise Shells“, you can remove floating sections. The smoothest fill patch can be achieved by manually filling large non-planar holes using the “Freeform” option found under Holes in the “Fix Wizard” menu. After manually forming a few bridging triangles, the “Ruled” option, which specifies a direction for the hole to follow, is used to span the cylindrical gap in one of the flower’s stamens.
The “Fix Wizard” occasionally fails to combine various mesh shells. When checked, this generates distinct meshes that can later be integrated using the “Tools > Boolean (Ctrl + B)” feature. On the main screen’s “Part Pages > Part List” menu, right-click the part and select “Shells to Parts” to correct the issue.
How to Repair STL Files with Free STL Repair Tools
Blender

A free and open-source environment for creating meshes that support 3D modeling, rigging, rendering, and animation is called Blender. The “Edit Mode” option under the “Mesh” menu in the lower toolbar offers many STL repair options. A “Mesh Analysis” tool is provided by the CellBlender add-on to assess manifoldness and search for manifold mistakes. Ensure the appropriate mesh or section is selected before starting repair scripts.
Triangles with inverted normals are flipped using the “Mesh > Normals > Recalculate Outside” command (Ctrl + N). Check the results in the info pane at the top. If quads were created, you could turn them into triangles by choosing “Mesh > Faces > Triangulate Faces (Ctrl + T)“. Edges and faces with no area are removed by “Mesh > Degenerate > Dissolve“. With “Mesh > Vertices > Remove Doubles“, remove duplicate vertices to join edges.
The quickest and easiest way to fill a hole in Blender is to first select the boundary loop using “Select > Select Boundary Loop” or all non-manifold edges using “Select > Select All by Trait > Non Manifold (Shift + Ctrl + Alt + M)“. Then, press “Mesh > Faces > Make Edge/Face (F)” or “Mesh > Faces > Fill (Alt + F)” By right-clicking an edge or vertex, Shift + right-clicking the next, and pressing F, you can make individual triangles. The “Vertex Select“, “Face Select“, or “Edge Select” modes, denoted by three icons at the bottom toolbar, can be changed while editing. With “Select > Circle Select (C)“, which functions similarly to a brush, a specific area can be selected. You can adjust the brush size with the mouse wheel or the numerical plus/minus buttons. To deselect, hold down the Shift key.
Sometimes “Mesh > Faces > Beautify Faces (Shift + Alt + F)” works to enhance mesh quality in the chosen region. Selecting a specific boundary loop requires pressing Alt + Right click. When “Mesh > Edges > Bridge Edge Loops” is set while there are two open boundary loops selected, the two areas will be seamlessly connected.
One object per shell will be created in the project browser by selecting “Mesh > Vertices > Separate > By Loose Parts“. Unwanted mesh objects can be removed as a result. Separate shells can be joined together with a “Boolean Modifier“. If all else fails, apply a “Remesh Modifier” and raise the octree depth to about 8 or until the desired results are obtained. Use the Inflate brush from the lower menu “Brush > Sculpt Tool” in “Sculpt Mode” to thicken the wall in specific places.
How to Repair STL Files with Free STL Repair Tools
Netfabb
A sophisticated 3D print file preparation tool, Autodesk Netfabb, has an automated repair feature built into programs like Formlabs PreForm. The first two versions are free for educational use and come in three different versions: Standard, Premium, and Ultimate.
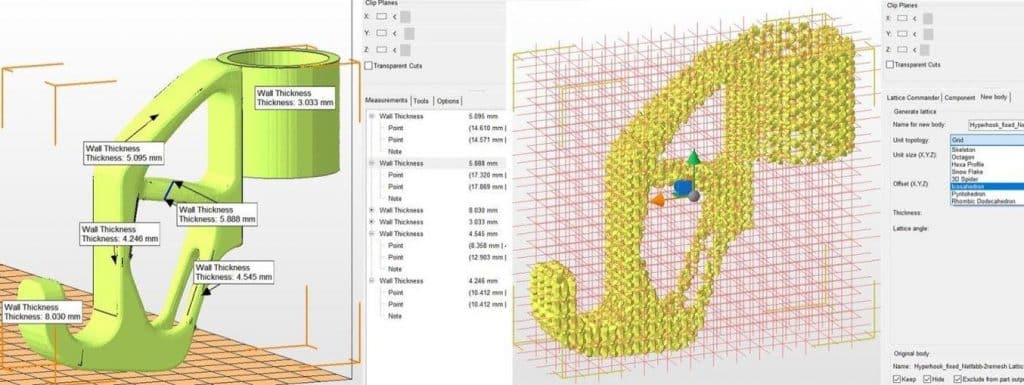
Additional mesh editing options provided by Netfabb include hollowing, creating custom supports, and using the “Lattice Assistant and Lattice Commander“, which are excellent tools for creating lightweight components. The “Optimization Utility” in the Ultimate version uses “FEA analysis” to structurally optimize parts based on applied loads.
It is possible to import mesh models in a variety of formats using the “File > Import CAD File” as “Mesh” function, as well as native files from Catia, Siemens NX, SolidWorks, SolidEdge, Rhinoceros, ProE, and Sketchup, as well as support for STEP, IGES, SAT, and Parasolid XT files. Select “File > Add part” and “Extended Repair” in the dialog box to import a mesh. This fixes the majority of issues and produces a 3D printable file.
Analyzing the parts is useful before beginning the repair. It is possible to quickly check wall thickness under the Analysis icon in the taskbar or after right-clicking on the part under “Parts > Analyse > New Analysis > Add part“. Simply right-click on the component, select “Analyze > New Measurement“, or select the ruler icon from the taskbar to perform point-by-point measurements of wall thickness, radius, and linear length.

By selecting the red Repair icon from the taskbar, you can access the “Part Repair” section. The “Mesh is Closed” and “Mesh is Oriented” items in the “Status” tab should be checked in green if the automated repair script performed its task successfully during import. You can further optimize the file in the “Actions” tab if there are any intersections. Select “Detect” under “Self Intersections” and then “Stitch Triangles, Remove Double Triangles, Remove Degenerate Faces, or Split Off” before selecting “Remove” to get rid of the intersections. Like voxelization techniques, “Wrap Part Surface” produces only a manifold outer skin. Additionally, confirm that the “Shells” tab is free of any noise shells.
Instead of trying to close gaps, Netfabb will fill the open holes that need more manual repairs. Select the entire hole by tapping the “Select Surfaces” icon on the main toolbar, then click “Delete“. Alternately, use the “Brush Selection” tool and adjust the brush size and selection using “Ctrl + Scrollwheel” and the “Plus/Minus” buttons. Choose the “Remove Selected Triangles” icon. In contrast, the triangles are selected, then manually add any missing triangles and a few bridging triangles using the “Add Triangles” button. The “Repair > Close all Holes” operation will finish the mesh repair task. The “Mesh Edit > Remesh” command allows us to choose to further refine the mesh by recalculating the model based on the “Target Edge Length” parameter. To improve model integrity near sharp edges, select “Maintain Edge“.
Searching for the ideal tool to bring your designs to life?
Let us know in the comments below or on our Facebook page to let us know your ideas, and we would appreciate seeing pictures of your works of art!






