Table of Contents
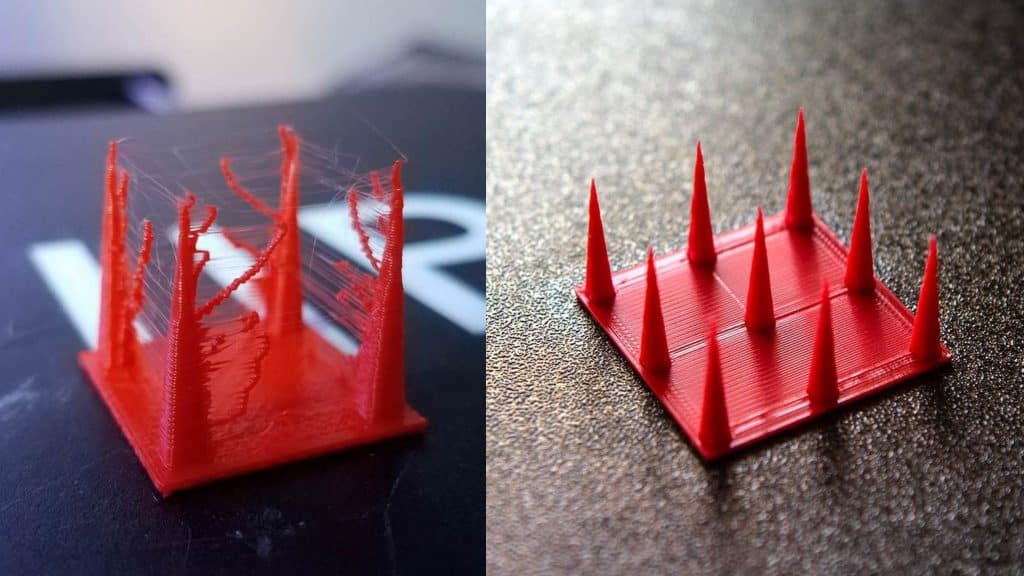
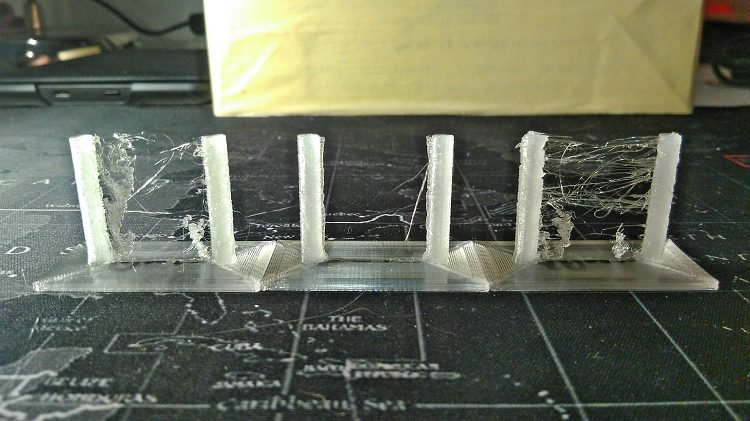
In 3D printing, stringing is a typical issue. Stringing, also known as oozing, happens when melted filament oozes out of the nozzle as it travels between two spots. This issue causes irritating “hairs” in prints that are difficult to erase.
Prevent PETG stringing requires a relatively high temperature to flow correctly. This higher temperature encourages strings to form, allowing the filament to freely flow between two sites.
This post will go through three methods for printing PETG without the strings.
11 Easy Ways to Prevent PETG Stringing Tip #1: Increase retraction speed
The extruder motor retracts a certain amount of filament from the nozzle. This procedure should eliminate any unwanted leaking on or between printed pieces. If you’re having trouble stringing, start by adjusting your retraction settings.
Start with a retraction speed of about 25 mm/s (for both Bowden and direct drive extruders) and a retraction distance of 6 or 7 mm for Bowden extruders and 3 or 4 mm for direct-drive extruders in your slicer’s settings.
If stringing persists, you can fine-tune these parameters in small increments until your printer’s retraction settings are correct. Increase the retraction speed in 5-mm/s increments at first, but be careful not to set it too high, or the nozzle will jam.
11 Easy Ways to Prevent PETG Stringing Tip #2: Reduce Nozzle Temperature
If adjusting your retraction settings doesn’t work, don’t worry. Put it another way, lower the temperature of your printer’s nozzles. Regardless of retraction or travel settings, it will ooze freely if your filament becomes too hot.
Try printing a temperature calibration block or a “temperature tower” to adjust your printer’s temperature. Most temperature towers come with guidelines for finding the ideal nozzle temperature with just one try! When determining the perfect temperature, keep in mind that you don’t want to sacrifice a smooth surface finish.
Also, check out how to print a temperature tower article.
11 Easy Ways to Prevent PETG Stringing Tip #3: Increase your travel speed
Increased travel speed is another easy treatment for PETG stringing. The less time melted filament has to ooze, the faster the nozzle advances between two spots.
Increase the travel speed of your printer in 10-mm/s increments until you find the perfect pace. Some manufacturers employ travel speeds as high as 200 mm/s.
11 Easy Ways to Prevent PETG Stringing Tip #4: Retraction Length
The retraction distance is another parameter that will require some trial and error to perfect. The retraction distance is how far the extruder retracts the filament into the nozzle (in millimeters). When the retraction distance is reduced, less filament is retracted each time the nozzle moves. When the retraction distance is minimal, there is more extrusion and stringing than when it is high.
You’ll have to experiment until you discover the perfect settings for retraction distance, just like you did with retraction speed. To gradually increase your retraction distance, use test prints. Do this until you observe a reduction in stringing and blobbing in your PETG 3D printing.
11 Easy Ways to Prevent PETG Stringing Tip #5: Speed of Printing
The print speed of a 3D printer refers to how quickly the print head moves during printing. Printing at a slower pace usually results in higher print quality. This is due to the printer’s ability to precisely extrude the material where it needs to go. On the other hand, fast print speeds make it difficult for the 3D printer to correctly extrude and put the melted filament.
However, increasing your print speed might assist if you’re having trouble with PETG stringing or blobbing. Slow print speeds allow your extruder to stay in the same spot for longer periods, giving your nozzle more time to leak filament accidentally. The best results are usually obtained when printing PETG filament at 40-60 mm/s.
While you should experiment with your settings until you discover the optimal print speed. Print speed should not be your primary concern when dealing with PETG stringing issues. While having a rapid print speed can help with stringing, it can also cause other problems.
When printing PETG, a print speed of less than 60mm/s is recommended. Changing your temperature and retraction settings first usually yields the most significant results.
11 Easy Ways to Prevent PETG Stringing Tip #6: Travel Time
Your travel speed differs from your print speed since it refers to how quickly your nozzle moves while not printing. If there is free space between two parts of your 3D print, your printer will not aggressively extrude as it travels through the gap. Excess filament has more opportunity to ooze out from one point to another when your travel speed is too slow, causing stringing.
Setting a fast travel speed decreases when your extruder is exposed to the elements, allowing it to ooze less. PETG filaments can be used at any travel speed; however, the faster, the better.
A rigid 3D printer with little moving mass, such as a CoreXY 3D printer, allows you to 3D print at speeds of up to 200 mm/s. On the other hand, budget 3D printers with an open frame are frequently limited to travel speeds of 100 mm/s or less. While these 3D printers can print at higher rates, you’re more likely to get ringing and other visual distortions.
You can set your travel pace significantly faster than your print speed without sacrificing quality. This is the case because it only affects places that aren’t part of your print. The nozzle will resume moving at your print speed as it reaches the next section of your build.
11 Easy Ways to Prevent PETG Stringing Tip #7: Combing
Combing is a function that helps you alter your travel pathways so that your extruder never goes across empty space if at all possible. Your slicer software recalculates how the extruder will move when you enable combing. The revised route guarantees that it stays as close as feasible to the paths in your actual print area.
This will increase the overall print time, but it is an excellent strategy to prevent PETG stringing. Combing can be a helpful remedy if adjusting retraction parameters, printing temperature, and rates haven’t decreased your stringing and blobs.
11 Easy Ways to Prevent PETG Stringing Tip #8: Vertical Elevation
Vertical lift (also called Z-hop in some slicers) is a retraction mechanism that generates space between the nozzle and the 3D print. It accomplishes this by elevating the print head slightly (or lowering the build plate). Because the nozzle isn’t touching the print as it travels, this can help you prevent strings. Any filament oozing won’t be able to anchor to one region of the print and leak material to the next.
11 Easy Ways to Prevent PETG Stringing Tip #9: Coasting
Suppose you’ve exhausted all other options and have trouble with PETG stringing and blobbing. In that case, coasting is another option to consider. When the printer is ready to travel through empty space, coasting turns off the extruder motor.
Any surplus filament in the extruder that would ordinarily cause stringing would be used to finish the current print portion. Before the printer reaches the conclusion of the print section, this will empty the extruder.
While this method may work if your stringing problem is severe, it frequently results in a line of under extrusion in specific print sections. This affects the print’s appearance as well as its structural integrity. As a result, it isn’t at the top of the list of PETG stringing options.
11 Easy Ways to Prevent PETG Stringing Tip #10: Wiping
Another function that can be used instead of or in addition to coasting is wiping. Before jumping from one point to another, the extruder travels around the print layer to “clean” off any excess filament on the extruder. The nozzle is less likely to leave strings or blobs behind because it has been cleansed of any excess material.
11 Easy Ways to Prevent PETG Stringing Tip #11: Use of a High-Quality PETG Filament
Using the best PETG filament brands can significantly improve your prints’ quality. The 3D printing process minimizes the quantity of PETG stringing, blobs, and other surface flaws. Reputable filament makers use high-quality raw materials and high-tech machinery to create their products. This ensures improved print quality consistency and an overall better 3D printing experience.
Filaments with tight tolerances can help you avoid extrusion issues on your printers. In most filaments, the acknowledged criterion for dimensional accuracy is +/-0.05mm. This means that the diameter may be 0.05mm less or bigger at different spots along with the filament roll than the marketed size.
Cheap filaments frequently have more significant diameter variances than the tolerances indicated on the package. Extrusion is uneven, resulting in PETG stringing and blobs. The extruder feeds in more material than the 3D printer controller board thinks it does when the filament diameter is larger than planned. It’s the contrary with filament that’s smaller than predicted in diameter.
Tolerances on high-quality filaments are generally significantly tighter. They often create filaments with tolerances of +/-0.03mm or +/-0.02mm in the case of Prusament. Your extruder will feed considerably more uniformly with that level of precision.
The essential ingredients utilized in low-cost filaments might also be a source of concern. Inconsistent melting temperature and viscosity are caused by low-quality polymers and additives. This makes perfecting your retraction, nozzle temperature, and other parameters extremely difficult, if not impossible.
Overture for PETG Filament Recommendation With +/-0.03mm tolerances, a 24-hour drying period before packaging, and a wide range of colors, PETG is our go-to PETG. It also prints at a lower temperature than typical PETG products, with a recommended extruder temperature range of 190°C-220°C. These are closer to PLA temperature ranges, making them easier to manage for many 3D printers.
Is PETG a good material for 3D printing?
PETG is the name of the FDM 3D printing material used in the modified version. PET has earned a reputation for being extremely adaptable. It’s cost-effective and dependable, and it provides consumers with a variety of designs and engineering customizations.
Is PETG more durable than PLA?
PETG is a more flexible and durable material than ABS or PLA.
Why is working with PETG so tricky?
PETG filaments do not flow and are difficult to extrude when the extruder temperature is too low during printing. As a result, printing with the correct nozzle temperature is critical.
We’ve reached the end of our knowledge on stopping PETG stringing. In fact, implementing the act rather than reading over it could be difficult and scary. As a result, test runs are essential for optimizing end results.
Once you’ve mastered the art of current technology, such as 3D printing for PETG, you’ll be able to accommodate and lead yourself in various ways. Customizing real-time art has never been more enjoyable or essential.